sacral torsion seated flexion test|sacral shear and torsion pain : member club Sacral torsions are commonly diagnosed by a review of medical history and a physical examination. During the physical exam, some tests may be performed, like a seated . GoreLover444. Gore Whatsapp/Telegram Group ? Where i can get share videos and suggestions !! Please i always wanted to chat with people with morbid curiosity !! Locked post. New comments cannot be posted. 56. Sort by: PersonaOfEvil.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 21 de fev. de 2024 · Por GIGA-SENA. O sorteio do concurso 3034 ocorreu no dia 21 de fevereiro de 2024 e o prêmio principal foi estimado em R$ 1.700.000,00 (um milhão e setecentos mil reais) para quem acertar o resultado da Lotofácil 3034. Quem acertar 14 (quatorze), 13 (treze), 12 .

sacral torsion exercises pdf
A crucial dynamic test for sacral dysfunction is the seated flexion test. With the patient seated, this stabilizes the innominate, allowing the assessment of sacral motion without . The two core tests that are often recommended to diagnose the position of the sacrum are the Sphinx Test and seated flexion test.⁶ ⁷ The following landmarks are typically recommended to be palpated and assessed: .Review the following diagnostic and treatment techniques related to sacral somatic dysfunction: Lumbosacral spring test Sacral palpation Respiratory motion test Seated flexion test Sacral .A seated flexion test determines the side of dysfunction if positive on one side. If the somatic dysfunction is a torsion, the seated flexion test is found on the opposite side of the oblique axis.
Sacral torsions are commonly diagnosed by a review of medical history and a physical examination. During the physical exam, some tests may be performed, like a seated .Sacroiliac Dysfunctions. Unilaterally flexed (sometimes bilateral) sacrum. Sacral torsions: L on L most common, 90% R on R. L on R. R on L. Testing for Sacral Dysfunction. 1) Seated flexion . Standing flexion test. Function: assesses sacroiliac motion; Position: standing; Procedure. Place both thumbs below the PSIS. Ask the patient to bend forward while standing with both feet firmly on the ground shoulder .
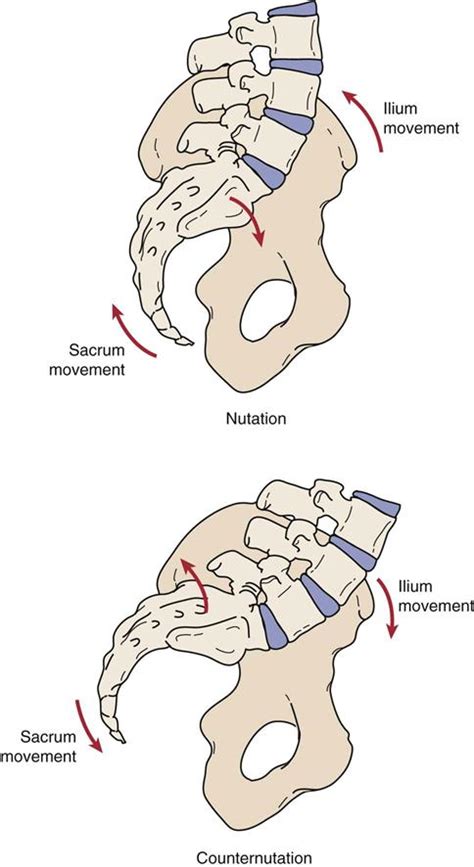
Common tests such as seated flexion and FABER should also be assessed. Beyond the physical examination, SIJ imaging can show varying levels of diagnostic accuracy in evaluating SIJ .Purpose of Test: To assess for sacral torsion. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The examiner palpates the sacral sulcus and inferior angle of the sacrum on each side, while the patient is in the prone position. Assess sacral sulci and inferior angles to see if they are symmetrical or asymmetrical. Have the patient move up onto his/her elbows, so he/she is .The standing flexion test is a test that can be used to assess . very little movement occurs (nutation and contranutation). It is a strong synovial joint, with both hyaline (on the sacral surface) and fibrous cartilage (on the ilial surface). Furthermore, the SIJ is reinforced by many ligaments .The side of the dysfunction is determined by the superior PSIS. Alternatively, perform the ASIS compression test, with the patient supine, by compressing bilaterally anterior to posterior at the ASIS. Lack of spring or restricted motion .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Identify the sacral axes about which motion occurs, including flexion & extension of the sacrum., Accurately describe postural motion of the sacrum and how it is used, along with respiratory cooperation, in the treatment of sacral flexion and sacral extension somatic dysfunctions., Accurately describe postural .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Upon examining the posterior landmarks of a patient's pelvis, you find the following: deep left sacral sulcus, left inferior/posterior ILA, right positive seated flexion test. Your diagnosis is? a. Left on right sacral torsion b. Left unilateral sacral extension c. Right unilateral sacral extension d. Right on left sacral torsion . A, Standing flexion test. B, Seated flexion test, sacral torsion. Positive test: Asymmetrical rise of one thumb above the other. Indicates: Restricted sacroiliac joint on the positive side. The seated flexion test isolates the sacroiliac joint by anchoring the ischial tuberosities to the table and taking out any hip flexion. This also removes .
Common tests such as seated flexion and FABER should also be assessed. . Restricted range of motion in the SIJ causing a torsion, flexion, extension motion pattern. . there is a negative straight leg raise test, but positive thigh thrust, sacral distraction, and sacral compression tests and presence of a focal point of pain 1 cm .The Seated Flexion Test is performed by having the patient sit on a level, low stool with feet flat on the floor, with the knees bent 90 degrees, and the feet shoulder-width apart. . I rarely find that a sacral torsion remains to be treated if the sequence of treatment is treating the lumbars before re-evaluating the sacrum and making a final .
The sitting flexion test is viewed by some authors 4, 14, 15 as a reflection of asymmetrical positioning (torsion) of the sacrum rather than torsion of the innominates, but data to support this hypothesis are lacking. Because the sacrum was not evaluated in this study, asymmetry of the sacrum might still be a factor and might explain the .
A crucial dynamic test for sacral dysfunction is the seated flexion test. With the patient seated, this stabilizes the innominate, allowing the assessment of sacral motion without the influence of the innominate bones. . it is diagnosed as a unilateral extension to the side of the positive seated flexion test. Anterior Sacral Torsion.
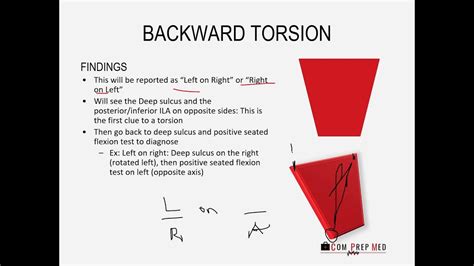
Tip For Simplifying the Sacral Diagnosis: Whichever side the seated test is positive on, the opposite oblique axis is the one that is engaged . For Example: With a positive seated flexion test on the right, then the LEFT oblique axis is engaged → you know it has to be right on left OR left on left OR unilateral flexion/extension on the right.
The sacral thrust test is a pain provocation test used to diagnose sacroiliac dysfunction. One single positive test does not have high diagnostic accuracy but a combination with other sacroiliac pain provocation tests gives valid evidence for sacroiliac dysfunction. The test is also known as: Sacral compression test; Downwards pressure testLumbosacralspring test Sacral palpation Seated flexion test HOURS 3 AND 4 Counterstraintreatments of various low back pathologies. . on L) sacral torsion the R edge is rotated L and anterior while the axis is left so it = to the SB side of L5. Sacral Motion In Non-Neutral (type 2) mechanics, theStanding flexion test 3. Supine to long sitting test 4. Prone knee flexion (Deerfield) test . right vs. left sacral torsion, etc.) that is often taught in most SIJ courses. However, since the individual tests themselves may have . This asymmetry suggests an issue with the sacral sulcus or sacral base. The Seated Flexion Test is particularly useful for identifying extension dysfunctions and issues related to the oblique axis of the sacrum. . To assess for sacral torsion, the practitioner palpates for asymmetry or rotation in the sacrum compared to the ilia. .
Sacral Torsion. Forward/Backward rotation on a Left/Right Oblique Axis. Forward Torsion. Flexed-same, same-L5 Diagnosis will be neutral. . A pt has a positive seated flexion test on the right, their right sacral sulci is more posterior and their left sacral sulci is more anterior. What is the diagnosis of the sacrum and L5?
sacral torsion diagnosis
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like diagnosing the sacrum, seated flexion test, what might a positive right seated flexion test mean? and more. . (rotated and sidebent to opposite sides), then you have a forward sacral torsion; negative spring and Sphinx tests If L5 is nonneutral (flexed or extended; sidebent and .Modified Seated Flexion Test: This Seated Flexion test is modified from traditional seated flexion test. Rather than using the PSIS for diagnosing, you use the sacral sulcus. Patient is Seated – both ischial tuberosities bear equal weight. Physicians fingers are placed over SI joint on the sacral side just medial to the PSIS at the level of .
Purpose: To assess the contribution of the sacroiliac joint to an apparent leg length discrepancy. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: The examiner grasps the patient's legs above the ankles and fully flexes them, then extends them. The examiner then compares the two medial malleoli to see if a difference in position is present. Have the patient sit up, while keeping the .Differences B/W unilateral sacral flexion and extension: 1. is the spring test (positive or negative) with flexion and (positive or negative) with extension 2. The sulcus is (deep or shallow) with flexion on the same side as positive seated flexion test, the sulcus is (deep or shallow) with extension on the same side as positive seated flexion test.HIP FLEXION AND FEMORAL POSTERIOR GLIDE FIXATION WITH LIMITED EXTENSION...81 SIDE GLIDE FIXATION OF THE PELVIS...83 Chapter 12 - THE MOST COMMON PATTERN OF LUMBOPELVIC . SPRING TEST FOR OBLIQUE AXIS SACRAL TORSION...116. P a g e | v Hesch Institute March 2012 www.Heschinstitute.org Email: .Question The iliosacral motion is thought to be diminished based on the findings of: 1 The standing flexion test 2 The seated flexion test 3 The lumbosacral spring test 4 The backwards bending test 5 The ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine) compression test, Which test is used to access sacroiliac motion?, A 27-year-old male is referred to the .
The Stork Test should not be the sole test used to diagnose SIJ dysfunction. The Stork Test demonstrates high reliability when a group of mobility and provocation tests are perform A meta analysis on intra-rater reliability reported the Stork test to have moderate to good agreement (κ = 0.46) Hungerford et al. concluded that the ability of the physiotherapist to reliably palpate and .Still University School of Osteopathic Medicine in Arizona, and private practice in Family Medicine in Tucson, Arizona Learning Objectives HOURS 1 AND 2 Review the following diagnostic and treatment techniques related to sacral torsion Lumbosacral spring test Sacral palpation Seated flexion test HOURS 3 AND 4 Counterstrain treatments of various .Sphinx position involves having the patient lie prone, then prop themselves up on their elbows to extend the lumbar spine and flex the sacrum (Figure 1).This can be very uncomfortable for extended or backward torsion sacral dysfunctions. See "Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction." Sims position is a modified version of lateral recumbent. Have the patient lie in the lateral .
Final answer: Establishing that the left ILA is higher and the seated flexion test is positive on the left, indicates a Left on Left sacral torsion dysfunction (also known as Left Axis on Left Rotation or L on L) in terms of osteopathic medicine.. Explanation: In this context, the terms refer to various landmarks and positional features of pelvic anatomy relevant in osteopathic .
length of polarimeter tube in decimeter
Resultado da Oliveira photos & videos. EroMe is the best place to share your erotic pics and porn videos. Every day, thousands of people use EroMe to enjoy free .
sacral torsion seated flexion test|sacral shear and torsion pain